Introducing the importance of looms in the textile industry:
A loom is a device or machine that is used to produce fabric, particularly woven fabric for the creation of textiles. This process is usually preceded by steps like opening, cleaning, carding, drawing and combing the yarn to prepare it for weaving. The yarn is also put through processes like spinning, winding, sizing and beaming. The weaving is finally done by interlacing the yarn and warp on the loom. There are two kinds of loom that run in the textile industry, namely handloom and power loom. Let us see how the two are classified and what the differentiating factors between the two are.
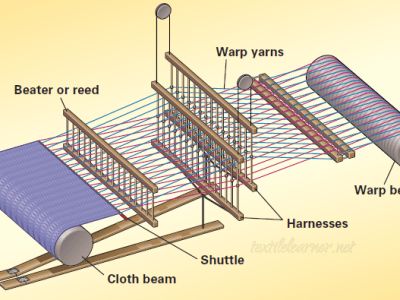
Basic Structure of a loom
Image source:- Pinterest
Details and History of Looms:
The weaving fabric was an ancient practice that was carried out to keep the culture alive and is dated back to the Maya civilization when the goddess Ixcehl taught women how to weave at the beginning of time. Since then, looms are used around the globe and have been evolving as early as 4400 BC in Ancient Egypt, and is now known to be the ‘titan of all fabric creation’ after it has proved their worth through centuries.
The evolution of the loom has been a critical factor for the textile industry, as well as the creation and evolution of fashion through the years. It is one of the main cultivating factors for turning thread and yarn into fabrics and textiles, which further assist the making of products like clothes, blankets, and anything that requires cloth fabric. The main operation of the loom has always remained the same, although, over the years, there have been some developments to improve the workings of the machine. One such advancement, and probably the most important one, is the introduction of the heddle to the structure. The heddle is a movable rod, which is used to raise the upper sheet of the warm that is used for weaving, and in later years, this piece was made into a cord or a steel band so that it could be used simultaneously.
Differences between Hand Looms and Power Looms
Handlooms are the kind of looms that do not require any electricity or power source to weave cloth, and are done on pit looms, as well as frame looms which are usually stored in the weaver’s homes. Created in the 13th century, it could be termed as more ‘primitive’ in comparison to its counterpart, power looms, but is equally useful.

Power looms are deemed to be more modern, and were initially adopted by the cotton industry in England. With the arrival of electricity at the start of the 20th century, the use of these machines increased. With more technology and advancements in the industry, modern industrial looms have the capacity to weave at 2,000 weft insertions per 60 seconds, or a minute. It works on electrical power and is used for manufacturing yarn to fabric pieces in a comparably short period of time. In this, the weft thread is pulled through the warp by a pressurized jerk or jet of either water or air.
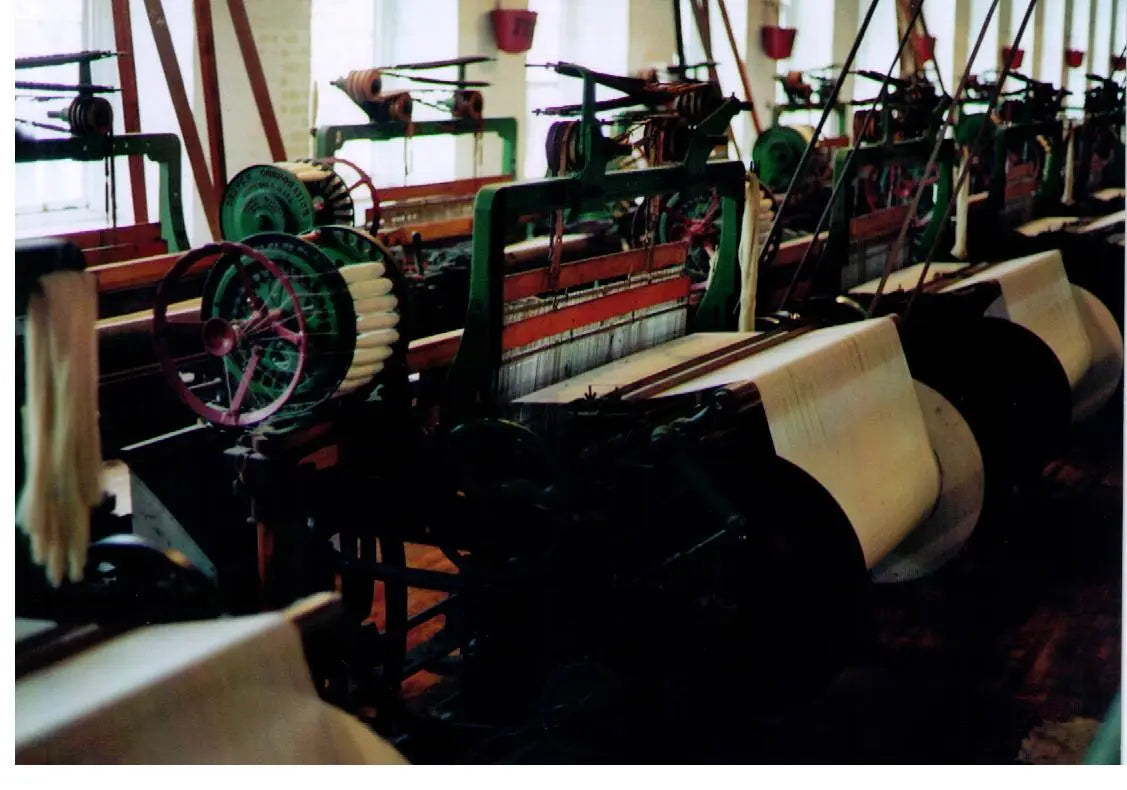 Image source:-Wikipedia
Image source:-WikipediaManually operated looms assist the artisans in creating unique and intricate clothing, with the finest quality, such as those that use hand looms. Most of the fabric that is produced using a power loom is deemed to be a replica of sorts and requires very minimal skill by the worker.
Fabrics made by the hand looms are more than often soft in their texture, and quite resilient, while a power loom has the tendency to produce fabrics that are stiffer and hard in feel, which is caused by compact weaving and spreading of the weft that takes place in the machine.

The reverse side of fabrics made by the handlooms is known to be a replica of the front, while that of fabrics by power looms, can observe a lot of loose threads and ends of the stitches, as it is not possible for them to weave that part when woven on the power looms.
The hand looms, performed manually by the artisans, tend to have some flaws, uneven surfaces, or thread pulls, while if the fabric is woven on the power loom, its texture and textile are flawless, but lacks allure and creativity, owing to the fact that it is machine made.
The level of intricacy and sharpness of the designs created by artisans cannot be matched by its competitor. Examples of this could be the work done for traditional Persian patterns like Ambi and Amru, which are beautifully delicate, and the detailing of it cannot be carried out on power looms.
The heavy- weight of the electric looms puts some pressure on the fabric results in it getting thinner, or thinning, which is not ideal for the fabric. Handloom items that may be made from the same material will be much heavier and have more body and strength.
The loose weaving of handlooms also makes it much more resilient and allows the fabric to breathe, unlike power loom weaving which is very tight.
Loom Made products available on iTokri
iTokri is a brand that was built on the motto of advertising and supplying Indian handicrafts and handloom products in order to help uplift the craftsmen and artisans and bring them into the spotlight. It is India’s only craft and looms retailer and is proud of this position. Most of the fabric products that are available on our website are made by handloom and we house a variety of these items. Some of these are Cotton hand loom shirts for men, as well as sarees for women, scarves, printed fabrics, short kurtis and stoles and towels among many others.

Blogs you might also like:
Know Your Handlooms
The Prehistoric Period Interest in Indian Muslin Fabric
 Verified Purchase
Verified Purchase






































Leave a comment (all fields required)